119. Pascal’s Triangle II
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal’s triangle.
In Pascal’s triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
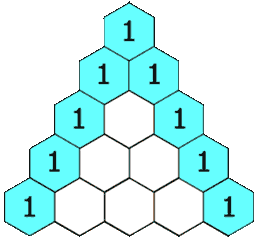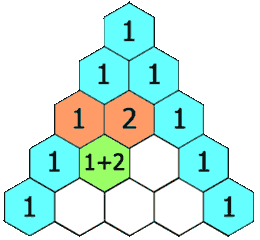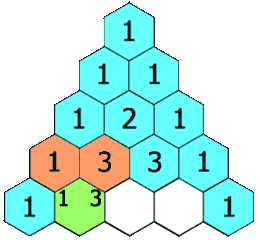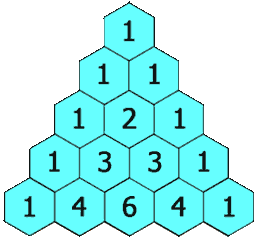
Example 1:
1
2
| Input: rowIndex = 3
Output: [1,3,3,1]
|
Example 2:
1
2
| Input: rowIndex = 0
Output: [1]
|
Example 3:
1
2
| Input: rowIndex = 1
Output: [1,1]
|
个人解答:
时间复杂度:O(rowIndex)
空间复杂度:O(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {
vector<int> ans_v(rowIndex+1);
for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
ans_v[0] = 1;
ans_v[i] = 1;
vector<int>temp_v = ans_v;
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) {
ans_v[j] = temp_v[j] + temp_v[j - 1];
}
}
return ans_v;
}
};
|
进一步优化(一个数组):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {
vector<int> row(rowIndex + 1);
row[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
row[j] += row[j - 1];
}
}
return row;
}
};
|
